Looking at Kalevi Kull and Ekaterina Velmezova’s Book (2025) “Sphere of Understanding” (Part 1 of 3)
SaH 0001 The full title of the book before me is Sphere of Understanding: Tartu Dialogues with Semioticians. The book is volume 23 of the series, Semiotics, Communication and Cognition, edited by Paul Cobley and Kalevi Kull, published in 2025, by Walter de Gruyter GmbH, Berlin/Boston.
Kalevi Kull is a biologist who joined the Department of Semiotics at the University of Tartu in 1997. Ekaterina Velmezova is a linguist and historian who graduated from Moscow State University. Each, in their own way, represents the two poles of the Tartu-Moscow School of Semiotics.
0002 The question is: Does this book mark the end of the first ascent or the beginning of the second ascent for the Tartu Moscow School of Semiotics.
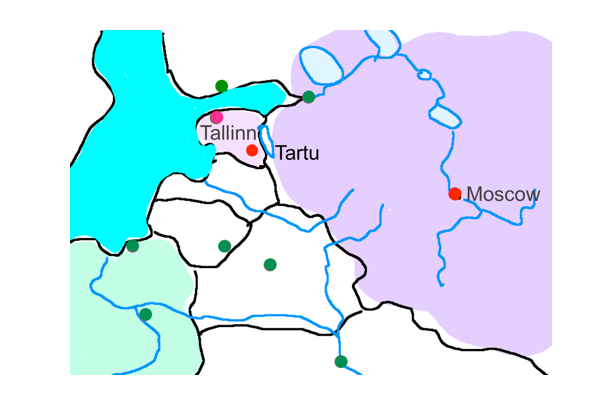
0003 After the introductory chapter, extolling the virtues of dialogue, the authors offer a brief history of semiotics in Estonia. The arrival of Juri Lotman, a scholar of Slavic literature, initiates a transnational collaboration within the old USSR. The summer school at Tartu University proves seductive. Here is a place where scholars in Slavic literature are free to play.
0004 So, one aspect of the sphere that the authors desire to understand is a historical conception, sired from the intellectual loins of Juri Lotman, that has taken a life of its own. The only question is: Who is she?
0005 Kalevi Kull wrestles with emergence in biological systems. What about this semiotically inclined child of history?
0006 Ekaterina Velmezova performs translation into English, as well as, I imagine, editing in Russian. After all, these are times when Estonians may want to hedge their bets.
0007 Who knows?
Can the Tartu-Moscow School of Semiotics be born again?
The interviews provide clues. They are gems framed in their historical moments.
0008 So how do I, a crypto semiotician, respond?
0009 First, I look at back issues of the journal that Juri Lotman founded, Sign System Studies, and find a special issue in 2017 bearing the title: Semiotics and History.
Second, I review several of the articles, plus one from 2016, in order to produce my contribution to the book’s dialogue.
Third, I package the results into an online independent mini-course, the first in a series titled, “Semiotics and History”, by Razie Mah, starting in December, 2025.
0010 The editors of the journal, Sign System Studies, have permission to scrape the blogs of this mini-course for a special on-line issue, as well as permission translate the blogs into other languages. After all, time is cruel. If the blog goes off-line, then the editors will retain a response that addresses what the authors seek.
0011 What do the authors seek?
0012 First, they seek a “sphere”. Shall I add… “of influence”? Or, shall I be satisfied with “of understanding”.
The interviewers ask semioticians questions. After the year, 2008, these queries include how the semiotician came into contact or awareness of the (first ascent of) the Tartu-Moscow School of Semiotics (1960s-1980s). The authors want to appreciate the school’s sphere of influence.
0013 Second, they seek understanding.
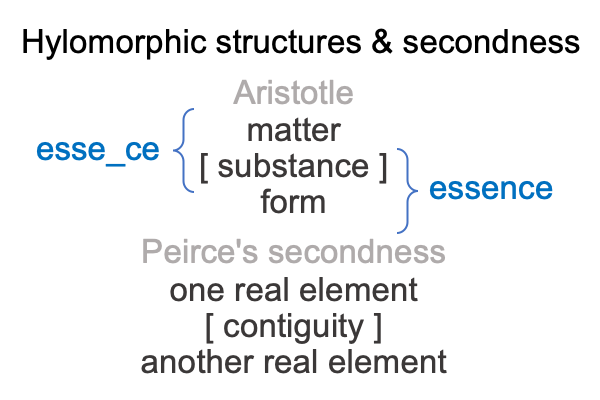
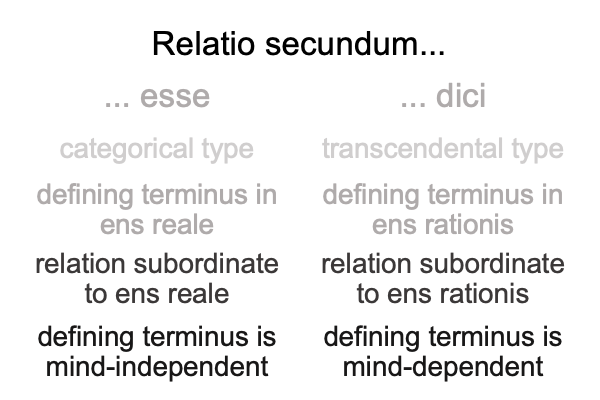
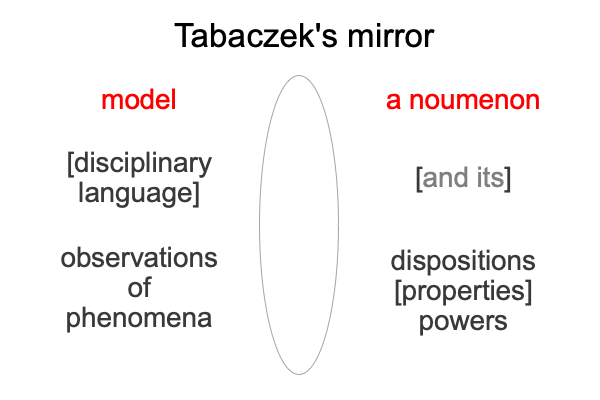
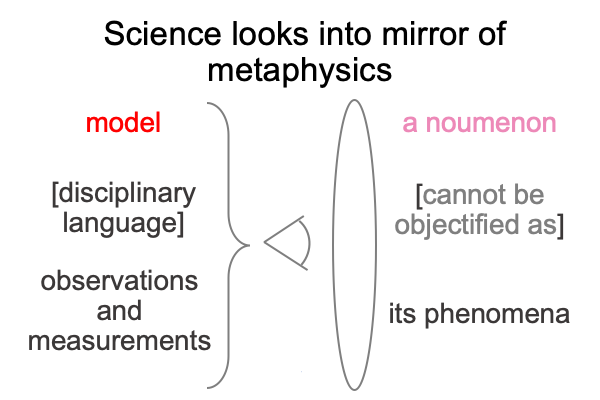
Here is where the discrepancy between Saussure and Peirce comes in. Today, practitioners of both traditions are called, “semioticians”. But, Saussure called his path of inquiry, “semiology”. And structuralism? Structuralism virtually situates semiology. Structuralism is semiology as matter substantiating aesthetics as form.
0014 So, what am I doing?
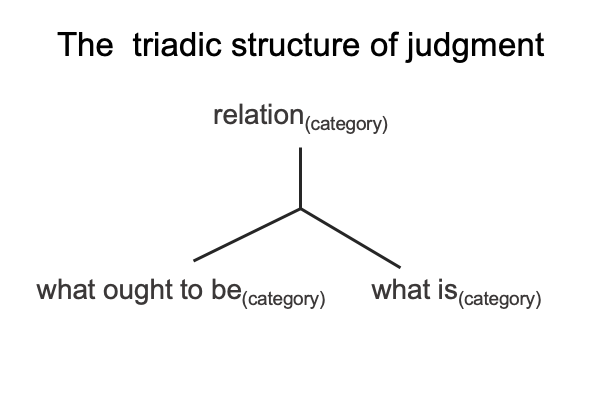
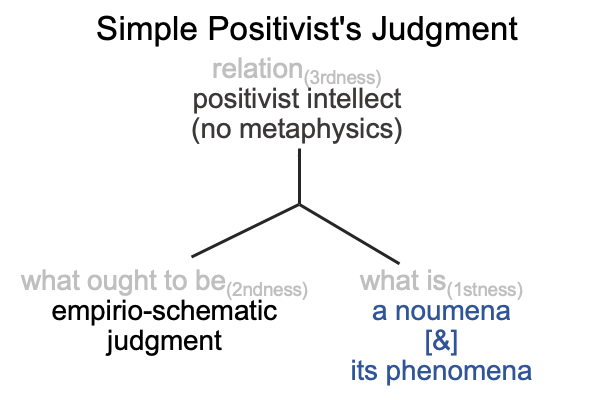
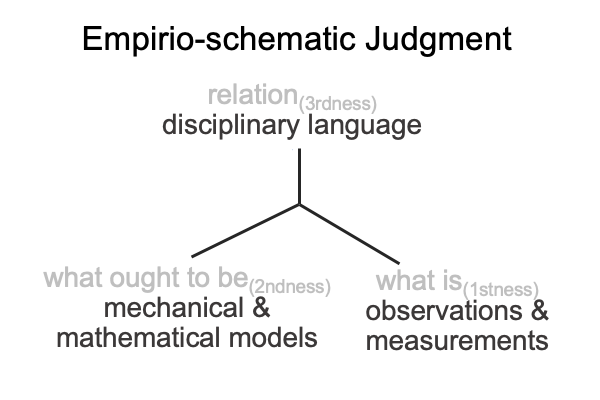
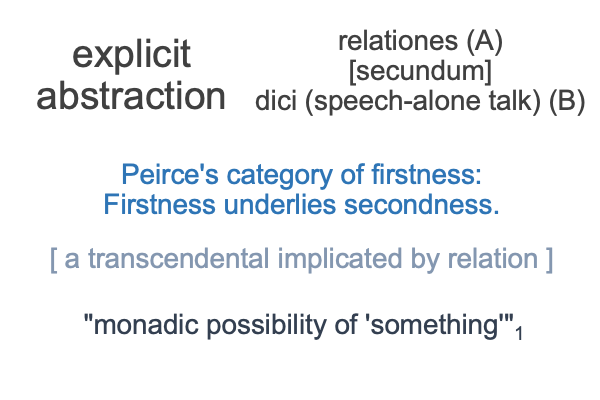
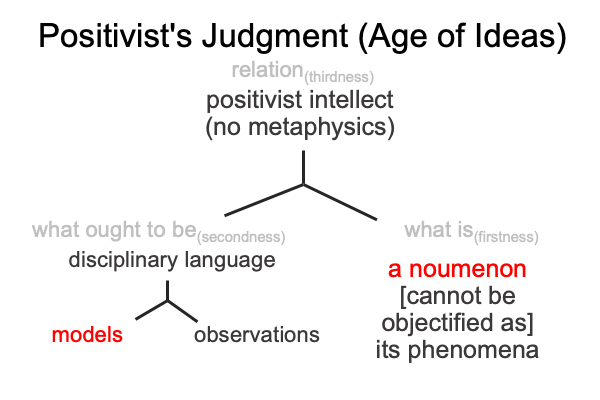
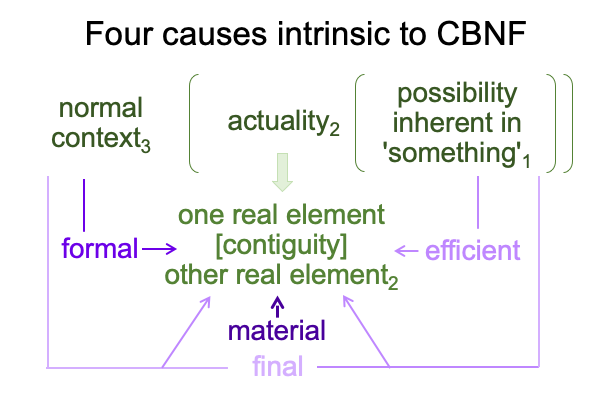
I follow the path of Peirce, into the labyrinth of triadic relations, and attempt to identify the normal contexts (thirdness) and potentials (firstness) of the actualities (secondness) of semiology and structuralism.
0015 What do I find?
I find that “she” is Slavic civilization, herself.
0016 My examination of articles in the 2017 special issue of Sign System Studies, titled “Semiotics and History”, pays tribute to the authors’ search, embodied in the title, and provides a way to understand the Tartu-Moscow School’s sphere of influence, for both the first iteration in the old USSR and its second iteration in the upcoming Eurasian convergence.