0222 With that said, here is a quick wrap-up of the four chapters in Part III.
For chapter six, Sharov and Tonnessen’s noumenal overlay conceptualizes semiotic agency.
For chapter seven, semiotic agency is considered an actuality2. In order to understand an actuality2, the actuality2 must have a normal context3 and potential1.
0223 Here is the nested form for semiotic agency2.
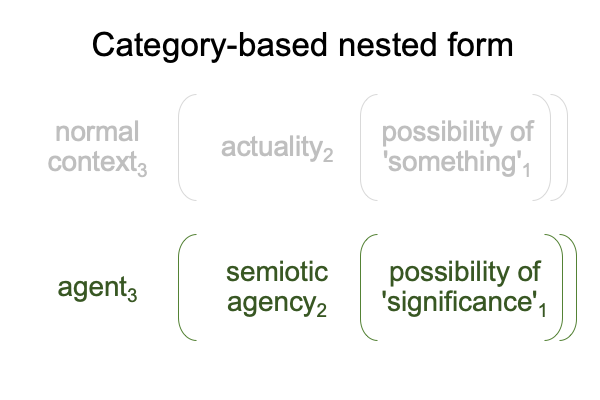
Semiotic agency2 presents a sign-relation as a dyadic actuality. This is shown in Part I.
Semiosis2 does not occur without an agent3 and the possibility of ‘significance’1.
0224 For chapter eight, the evolution of agents3 and the possibility of ‘significance’1 proceeds in tandem with the evolution of semiotic agency2.
0225 For chapter nine, phenomenology serves as a precursor to biosemiotics, just as the social sciences of the nineteenth and twentieth centuries serve as intimations of phenomenology.
0226 Without a doubt, Sharov and Tonnessen build upon the insights of philosophers writing a century earlier, as seen in two of Razie Mah’s e-books: Comments on Jacques Maritain’s Book (1935) Natural Philosophy and Comments on Nicholas Berdyaev’s Book (1939) Spirit and Reality. Both Maritain and Berdyaev are interested in understanding the nature of scientific inquiry. And now, their works inform biosemioticians.
