531 The text before me is chapter four of Semiotic Agency (2021). Details on the text may be found on point 0473. Chapter four covers pages 95-122.
0532 This chapter is an overview of both hierarchy and the evolution of living systems composed of hierarchies of sub-agents.
0533 Section 4.1 concerns a gradation of competence in semiotic agency. The gradation arises from the intuitively obvious structure of animals.
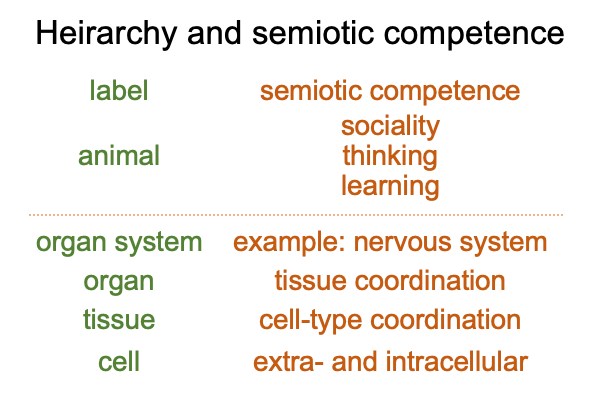
0534 The above picture suggests that each level of semiotic competence both encompasses and transforms the adjacent lower level.
0535 Does the adjacent lower level come under the control of the higher level?
It makes me wonder about the term, “control”.
Does “control” assume the functionality of adjacent lower-level subagents?
Does “control” indicate that the higher-level agent uses lower-level subagents in order to achieve its goal?
0536 Well, here is one way to diagram the relation between agent and subagent.
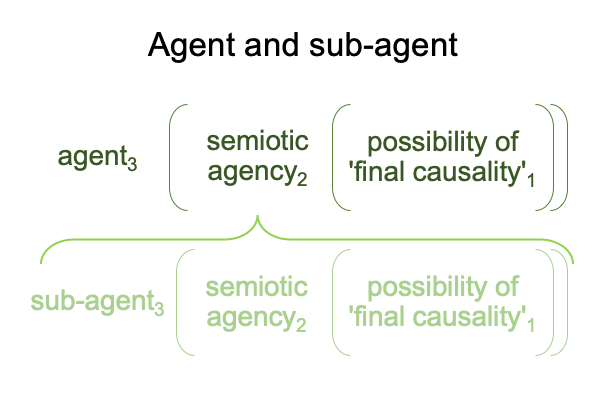
The agent relies on the subagent to behave like its supposed to behave.
Does that accord with the meaning, the presence and the message of the word, “control”?
Yes, the agent uses the subagent and assumes the functionality of the subagent.
But “control”?
0537 Is there any other term that applies to the metasystem transition implied by the above figure?
Take a look at the normal contexts.
The logics of thirdness are exclusion, complement and alignment.
How do these apply to the above figure?
Obviously, the relation between the agent and subagent is one of alignment. This implies that the possibility of ‘final causality’1 for the agent3 is included in the possibility of ‘final causality’1 for the subagent3. Otherwise, the subagent3would be excluded from the agent3.
0538 Well, what about the other two logics?
Surely, exclusion and complement must have roles to play.
They do, in an evolutionary schema.
Recall, biological evolution is a mystery, consisting of the intersection of adaptation and phenotype. If evolution starts with an agent, and ends up as agent with subagents, then the subagents differentiate (exclusion), specialize (complement) and then align (alignment). If evolution starts with an independent agent (exclusion), who ends up as a subagent within another agent, then maybe some sort of phenotypic change comes into play (compatibility), leading to incorporation (alignment).
0539 Here is a picture of both routes.

0540 Consider the domestication of the dog.
Can I imagine the logics of exclusion, complement and alignment in play?
The agent is like an Umwelt to the subagent. The subagent participates in the Innerwelt of the agent.
