Looking at Alexander Kravchenko’s chapter (2024) “A Constructivist Approach…” (Part 2 of 6)
1005 On top of that, in chapter seven of Pathways, Alexei Sharov offers another option.
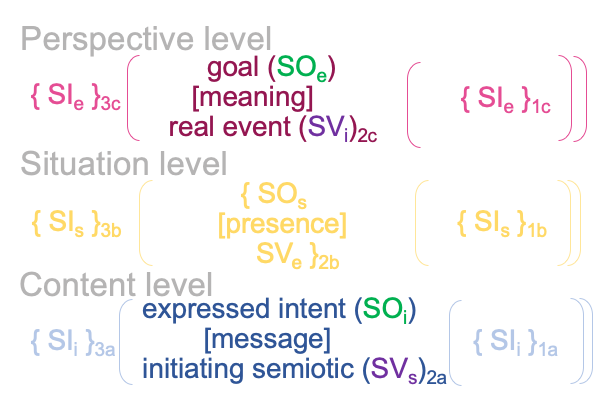
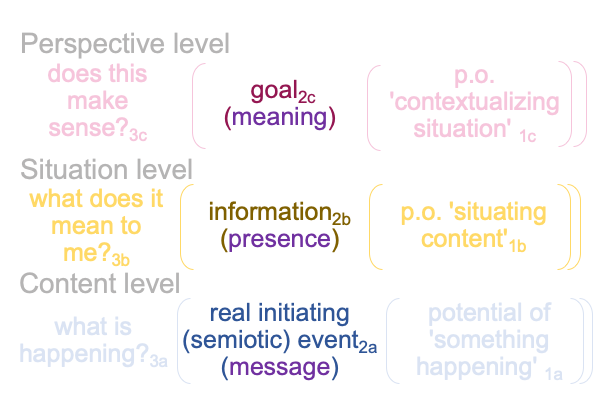
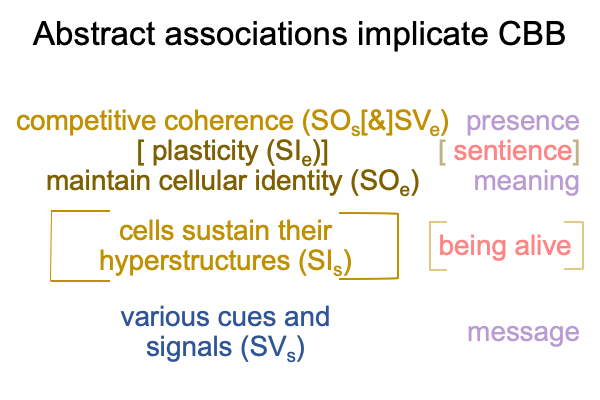
In addition to [meaning], there are potential meanings and potential signs. Potential meaning goes with [presence]. Potential sign associates to [message].
This is awkward, since the terms, “potential meanings” and “potential signs” take the contiguities out of their brackets (so to speak).
1006 Plus, the exercise of considering “potential meaning” and “potential sign” raises a question concerning how to square the normal-context of agent3 with the normal context of definition3. To me, the agent3 contextualizes definition2(3) as integral to semiotic agency2. So, somehow, the nature of spoken words2(2) gets imported into semiotic agency2 as a thing itself (or, should I say, “a noumenal overlay itself”?).
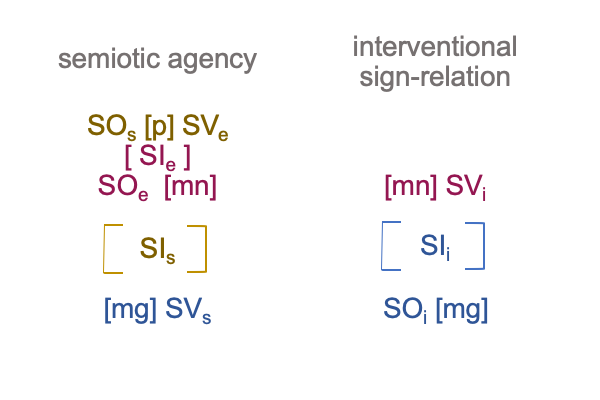
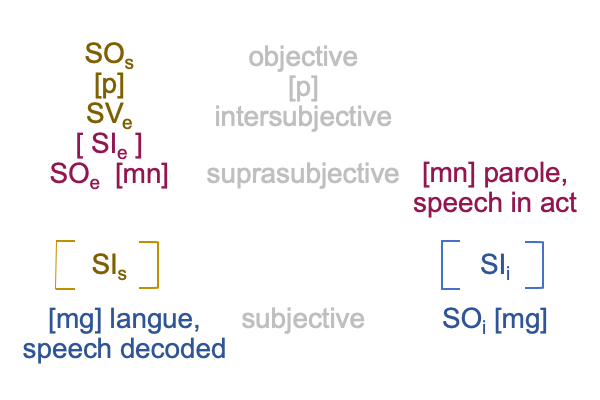
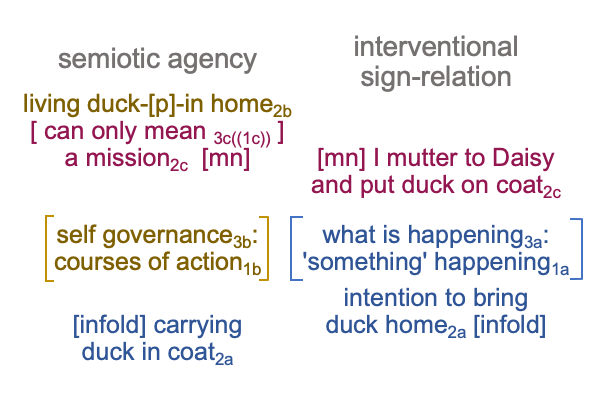
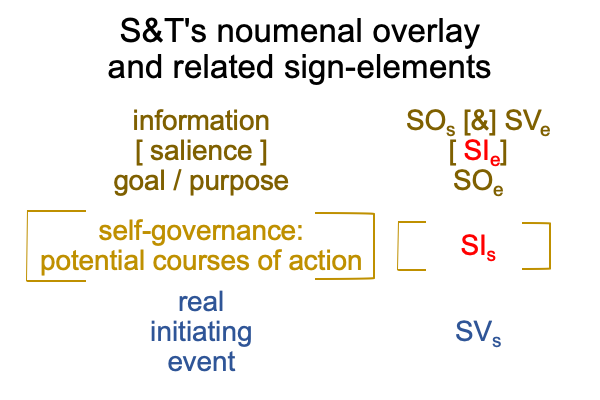
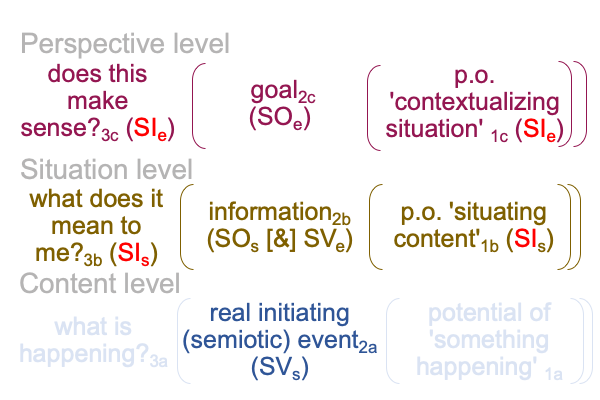
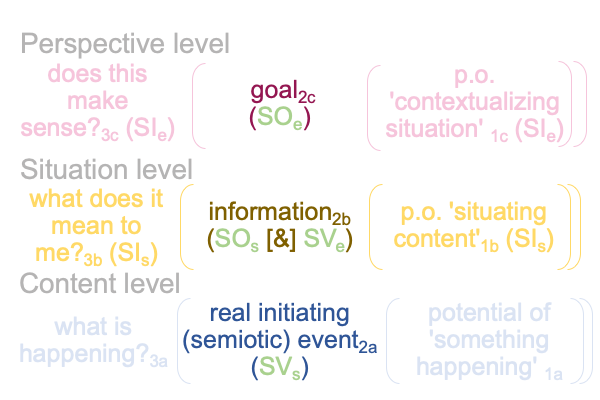
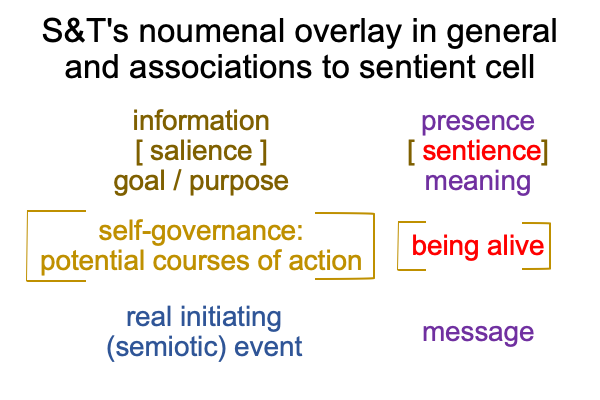
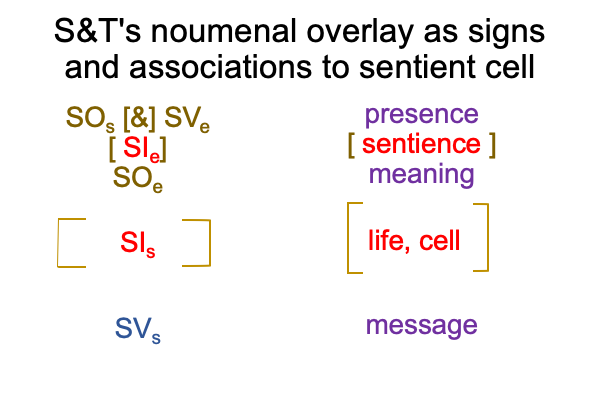
1007 Here is a picture.
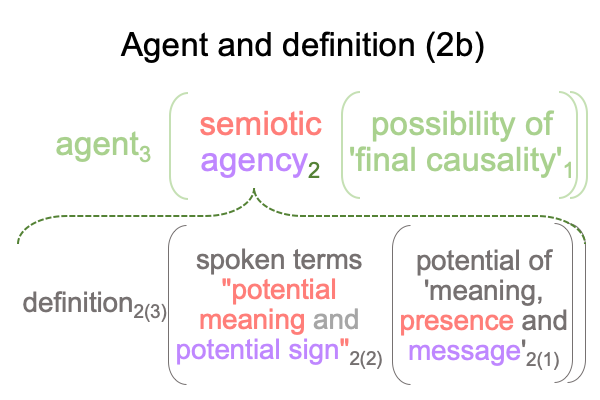
The colors are suggestive, but misleading. [Presence] is wholly contained within the semiotic of semiotic agency. [Message] spans interventional sign-relation and semiotic agency. The coloration reminds me that [message] is like passing through a portal to the SVs. An interventional sign-object (SOi) [inters or infolds] the specifying sign-vehicle of semiotic agency (SVs).
Here is the trick. With [inters], the SOi enters from the Umwelt. With [infolds], the SOi arrives from the Innerwelt. [Inter] is not wholly contained within the agent. [Infold] is.
That may be confusing. And, the above figure exploits that confounding with suggestive, but misleading, coloration.
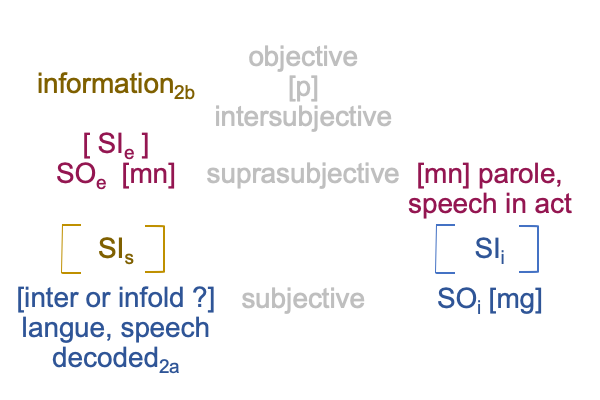
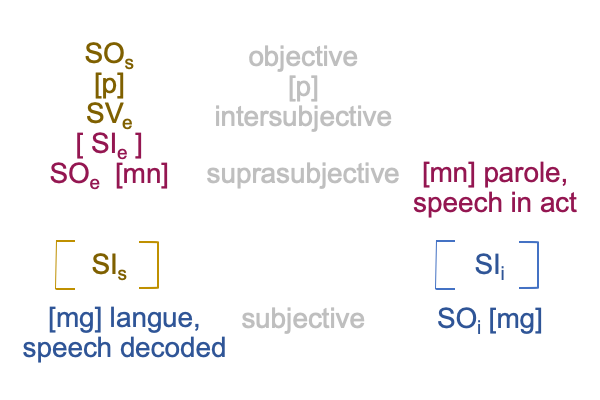
1008 What I have said concerning how [meaning] may be problematic fits the author’s bold assertion: Knowledge is a language game.
Meaning is like a substance, the contiguity between a manner of matter (the object of an exemplar sign-relation, SOe) and a manner of form (the vehicle of an specifying sign-relation, SVs).
Like [message], [meaning] is a portal. The portal goes from the end terminus of semiotic agency, the goal2c (SOe), to the beginning terminus of the interventional sign-relation, the goal in action2c (SVi).
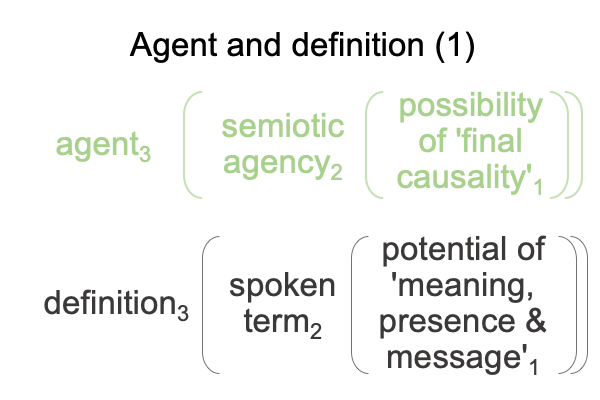
1009 At the same time, meaning1 is a potential that underlies a spoken term2 in the normal context of definition3.
1010 So, which is it?
Let the language games begin.
1011 The author relates that a century ago (say, around the 1920s, when the nature of empirical science is debated), linguistic theories of meaning display two fashions. One academic style concerns how spoken expressions work in terms of symbol manipulation. The other academic style concerns whether spoken expressions mean what dictionaries say they mean… that is, “semantic content”.
The author makes this accusation in section 8.1, titled, “Do We Ask The Right Kinds of Questions?”
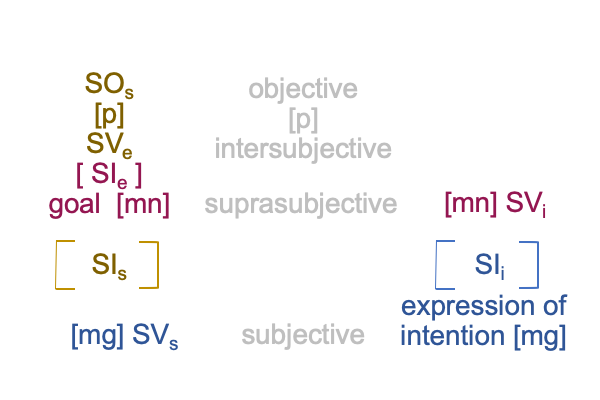
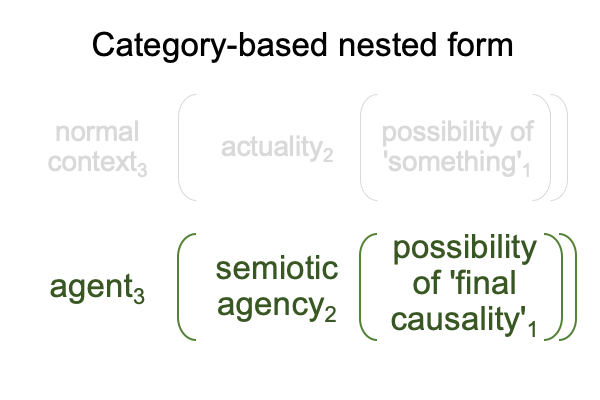
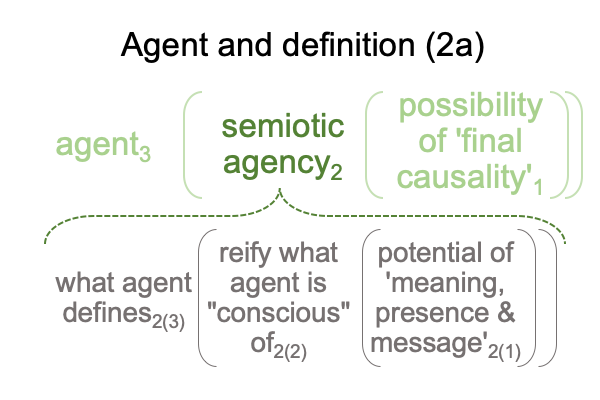
1012 I find this a little funny, along with the author’s note, saying (more or less), “Human adaptive behaviors3 may be viewed as end-directed activities that construct semiotic agency2 as a capacity1 to generate such behavior3.”
Without the subscripts assigning Peirce’s categories, the note sounds perfectly circular.
With the subscripts, the statement transforms into a category-based nested form responsible for constructing semiotic agency2 as an actuality2.
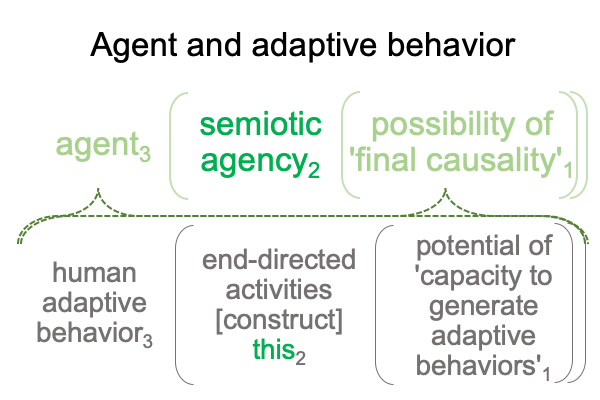
This2 is semiotic agency2.
1013 Here is the trick. “End directed activities” substitutes for “the interventional sign-relation”.
So, the interventional sign-relation [constructs] semiotic agency.
This dyad is a wonderful way to portray the biosemiotic noumenal overlay in speech-alone talk.
1014 Speech-alone talk is different from hand and hand-speech talk.
Hand talk pictures and points to its referents.
1015 In human evolution, hand talk becomes linguistic when manual-brachial icons and indexes become sufficiently distinct from one another as to constitute a system of differences.
Remember dictionaries? They embody a system of differences. Each written word differs from all other written words. Symbols constitute systems of differences. A finite set of symbols constitutes a symbolic order. The symbolic order represented by a dictionary is… um… alphabetical.
Once routinized, manual-brachial gestures become symbols, they fall into a system of differences and become linguistic. Then, these linguistic gestural-words support grammar. Grammar consists in symbolic operations within a finite system of differences.
So, hand talk refers by way of Peirce’s natural signs of icons and indexes (SOs). Also, hand talk becomes linguistic when these icons and indexes become more and more symbolic (that is, distinct from one another). Grammar consists of symbolic operations among hand-talk words.
1016 Hand and hand-speech talk belong to the Lebenswelt that we evolved in.
Speech-alone talk belongs to our current Lebenswelt.
Speech-alone words cannot picture or point to their referents.
1017 Speech-alone talk simply attaches a label to…. whatever… such as what the term, “end-directed activities” is supposed to mean. Or, maybe I should say, mean, present and announce.
The spoken term, “end-directed activities” announces, “I am what constructs semiotic agency”.
The same spoken term presents itself as belonging to the realm of actuality2.
The same spoken term has a meaning2 that arises from the potential of ‘the human capacity to generate adaptive behaviors’1 in the normal context of human adaptation3.
1018 So, here is the trick. The term, “end-directed activities”, is just a label.
The interventional sign-relation [constructs] semiotic agency.
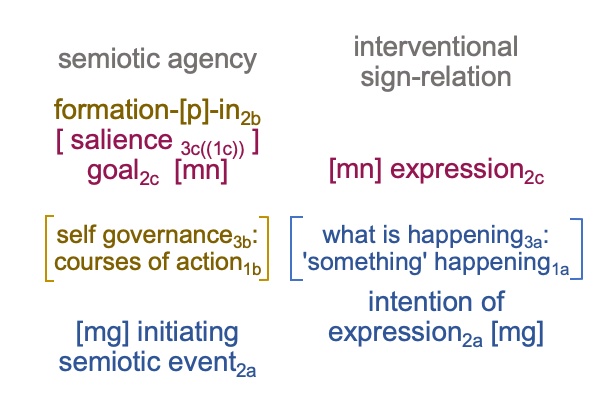
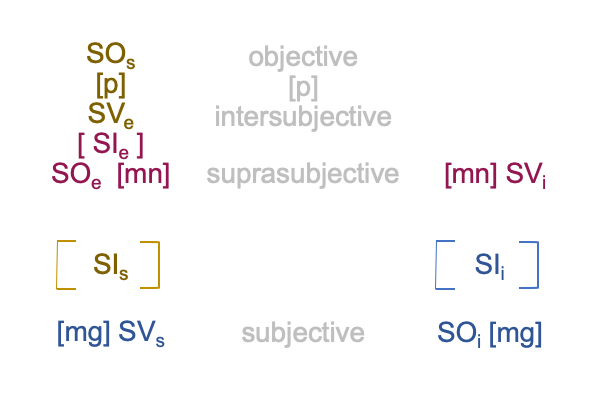
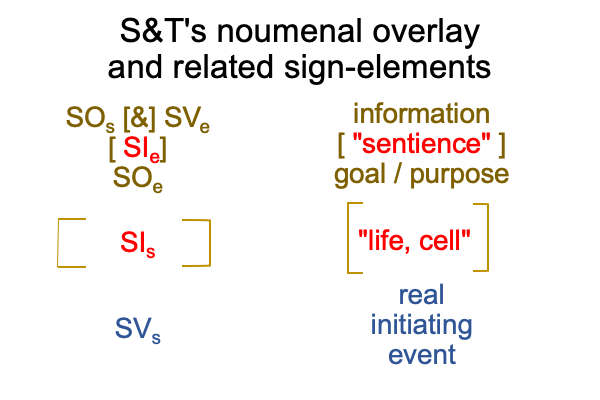
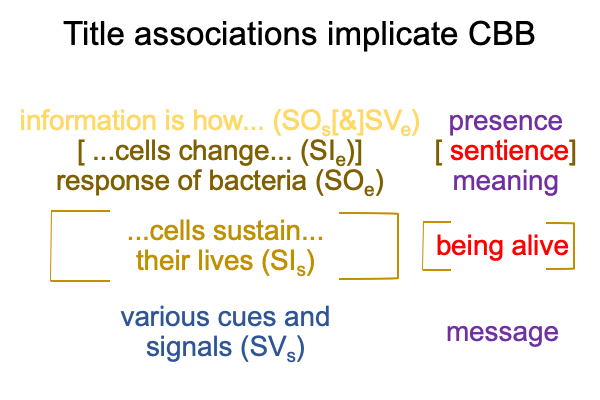
1019 Here is a picture.
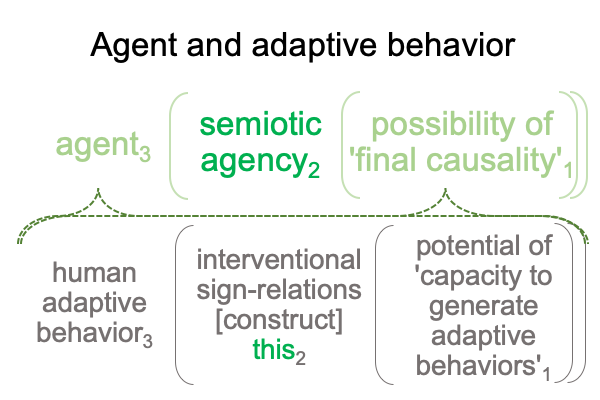
1020 The interventional sign-relation allows us to imagine that end-directed activities reside “out there”.
But, [meaning] draws the inquirer’s gaze away from the end-directed action (SVi) back to the goal2c (SOe).
And, this is crucial, because the goal2c resides “in here”, within semiotic agency.