Looking at Josh Hammer’s Opinion Piece (2021) “…Experts” (Part 4 of 4)
0019 Second, I look at the confounding of the sovereign and institution levels of the society tier, implicit in Josh Hammer’s opinion piece, and intrinsic to BG(il)L corporate media’s use of the word, “expert”, in reference to a federal bureaucrat.
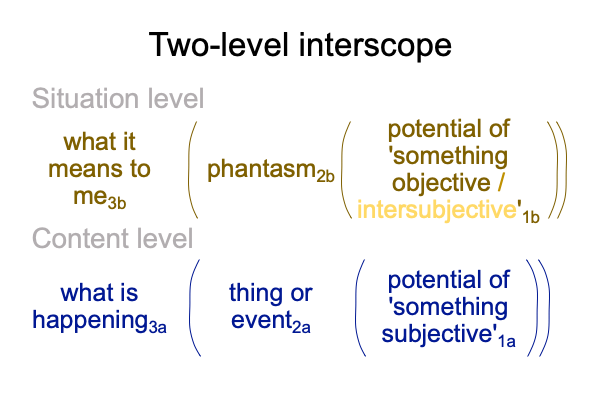
0020 The following two-level interscope portrays the first two levels of the society tier. The interscope for the society tieris developed in the masterwork, How To Define the Word “Religion”, available at smashwords.
0021 Here is a diagram.
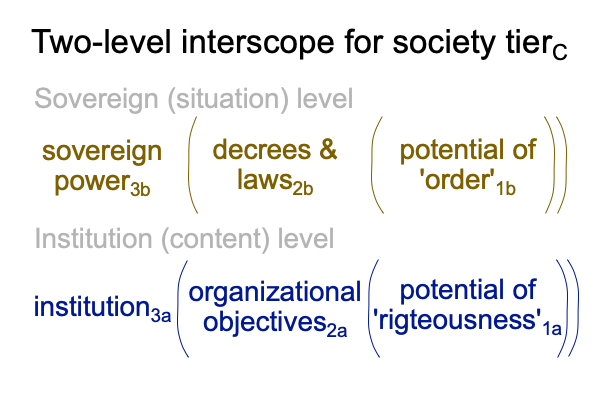
0022 According to the first paragraph of Josh Hammer’s opinion piece, bureaucrats exercise federal power2b within the “bowels” of the administrative state3bC. They do so by filling in legislative ambiguities and authorizations2bC. Bureaucratic decrees2bC establish the order1bC that vague legislation2bC mandates.
0023 How do federal bureaucrats develop their rule-based protocols?
They follow their “guts”… I mean… their “experts”.
0024 Of course, the metaphors of bowels and guts point to digestion. Digestion nourishes the body. What body? The administrative state?
0025 So, I ask, “What if the administrative state is a body?”
Well, the body is animated by a soul.
What is the soul of the administrative state?
0026 Well, why do the legislators pass vague laws2bC that authorize federal bureaucracies to do what they deem appropriate in order1bC to achieve certain organizational objectives2aC?
They do so on the basis of righteousness1aC.
0027 Does this imply that the Congress confounds the potential for order1bC with the potential for righteousness1aC?
Yes, for the past century, Congress establishes institutions3a within the federal government3bC on the basis of righteousness1aC, leaving the (federal) institutions themselves3aC to fill in the details of the authorizations2bC.
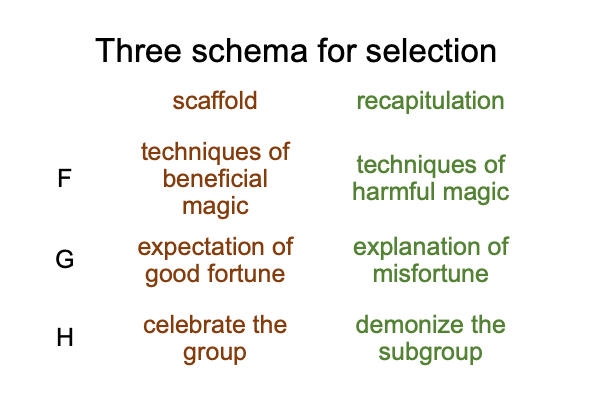
0028 This confounding constitutes one of two types of religion. Infrasovereign religions are institutions3aC arising out of righteousness1aC and bounded by the necessity of order1bC. Sovereign religions are institutions3aC that require (and exercise) sovereign power3bC in order to implement their organizational objectives2aC.
The other type of religion is suprasovereign3cC.
0029 While Josh Hammer’s point concerns the manipulative use of the word, “expert”, to refer to a federal bureaucrat, there is a deeper current in his opinion. Vaguely-worded legislation authorizing bureaucracies to fill in the details2bCconfounds order1bC and righteousness1aC and constitutes the formation of a sovereign religion3aC. Such legislation2bCviolates the first amendment of the Constitution, forbidding the federal government from establishing a religion.