0009 Now, I regard Kemple’s article “Signs and Reality”, in the journal, Reality, and Razie Mah’s Comments on Brian Kemple’s Essay (2020) “Signs and Reality” (available at the smashwords website).
Is there a crack in the mirror of the scholastic world, as it reflects on res (thing)?
Things are real.
So are sign relations.
If so, are sign relations things?
0010 If sign relations are real, then the consequences of their realness cannot be denied.
This if-then statement applies to biology.
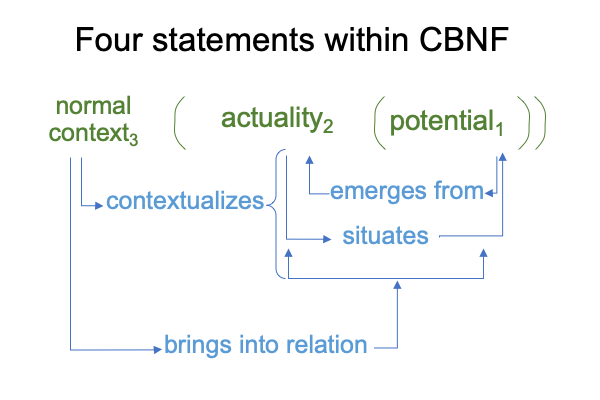
Are sign-relations so real that they are able to support a niche, into which some hapless creature may adapt? A niche is the potential of an actuality independent of the adapting genus. Could sign-relations, or triadic relations in general, be so real as to constitute a niche?
Consider the masterwork, The Human Niche.
0011 There are more consequences.
If sign relations are real, then a cultural change in the natural-sign character of talk may account for a rapid, inexorable alteration of a Lebenswelt. Does such a transition explain why our current Lebenswelt is not the same as the Lebenswelt that we evolved in?
Consider the masterwork, An Archaeology of the Fall.
0012 Finally, if our current Lebenswelt turns the evolutionary progression upside down, elevating stipulation over custom and custom over nature, then how do we validate our spoken words? If the meaning, presence and message underlying a spoken word is stipulated, upon what thing do we staple our stipulation? How about this: If we construct an artifact, then that artifact should validate our stipulation. The artifact validates what we stipulate it to be.
What can go wrong with that?
Consider the masterwork, How to Define the Word “Religion”.