Looking at Slavoj Zizek’s Book (2024) “Christian Atheism” (Part 23 of 33)
0245 So, what is the corresponding symbolic level?
Here is my guess.
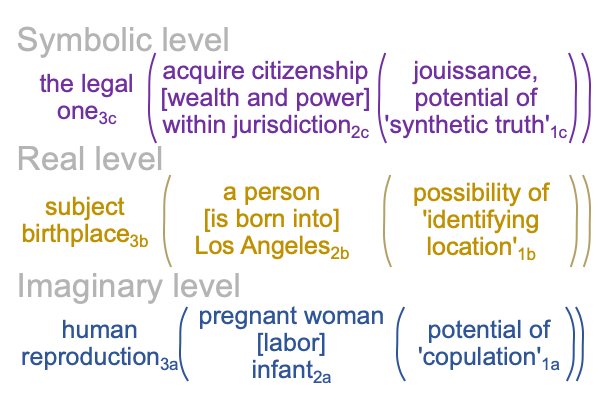
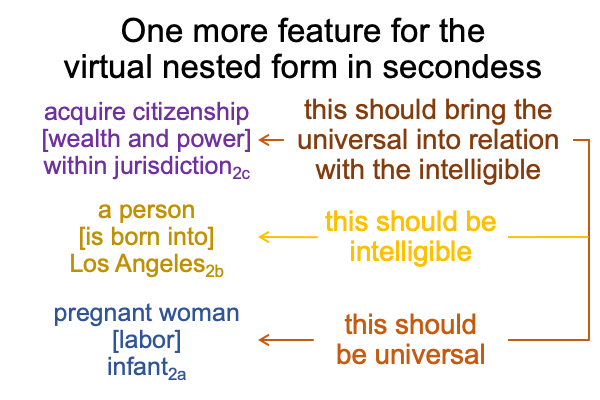
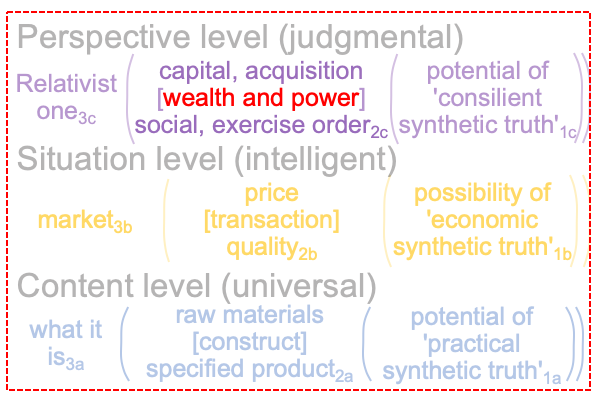
0246 On the imaginary level, the normal context of human reproduction3a brings the actuality of the dyad, {pregnant woman [gestation and labor] mother and infant}2a, into relation with the possibility of human copulation… and… conception1a.
On the real level, the normal context of the subject’s birthplace3b brings the actuality of the dyad, {a person [is born in] Los Angeles}2b, into relation with the potential of a location, where “location” is a mundane jurisdiction1b.
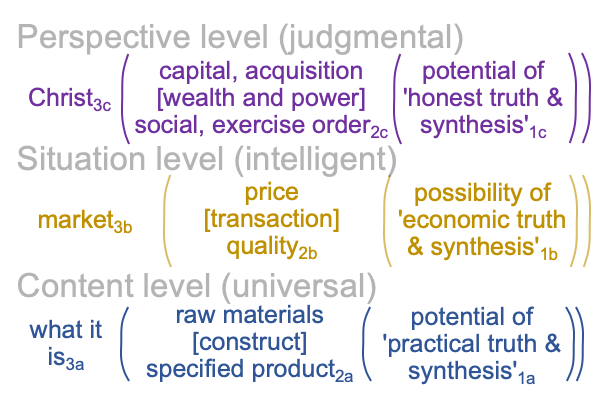
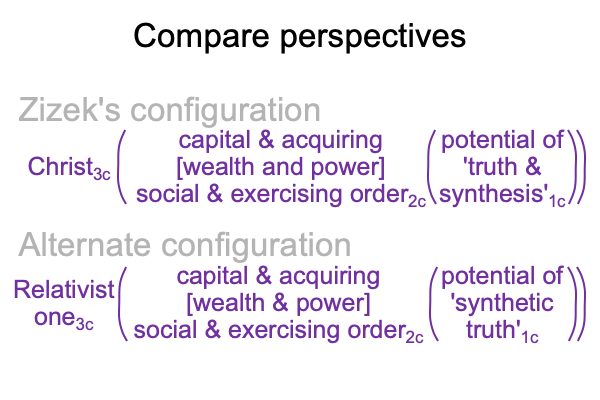
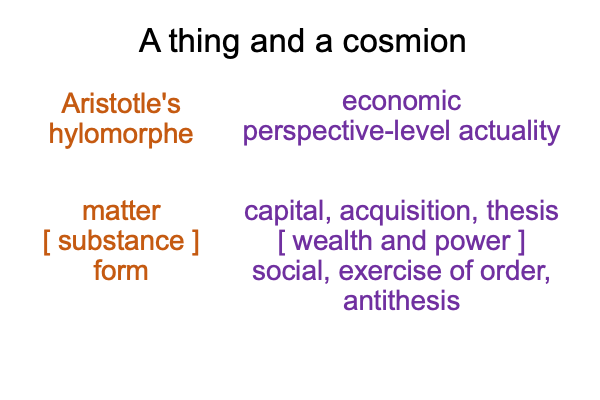
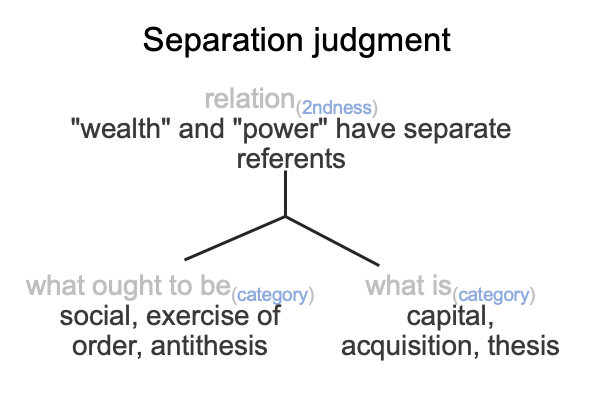
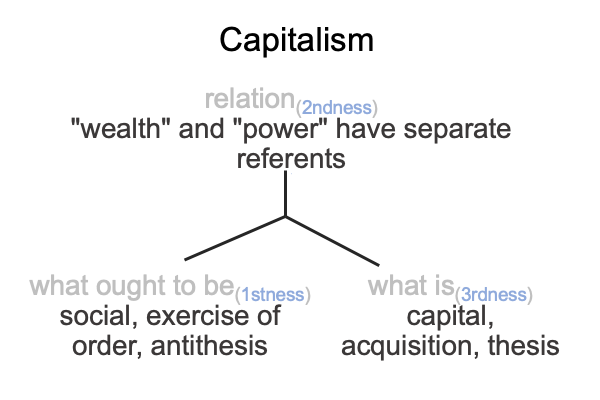
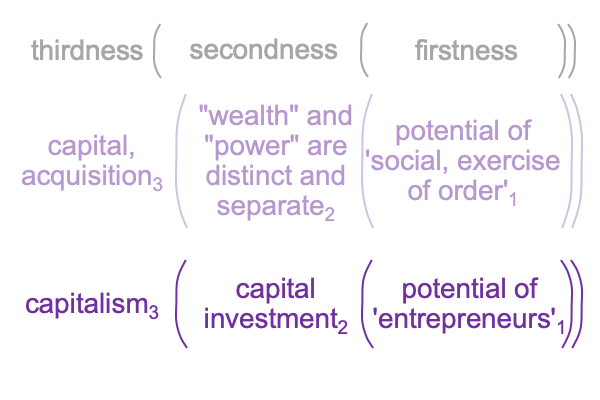
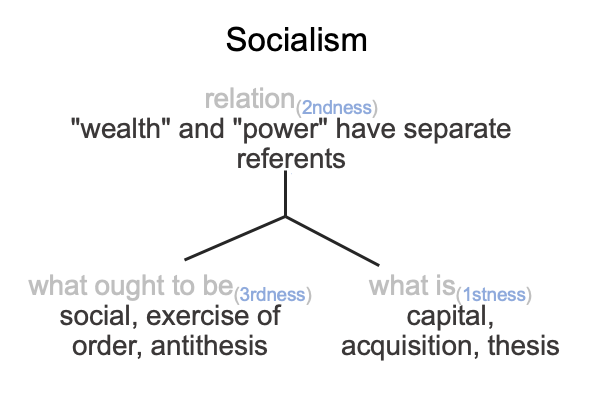
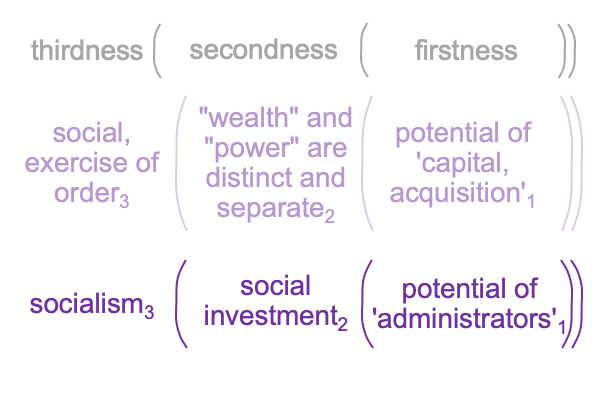
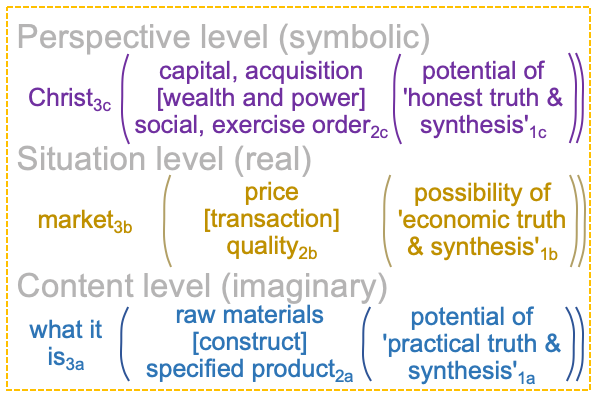
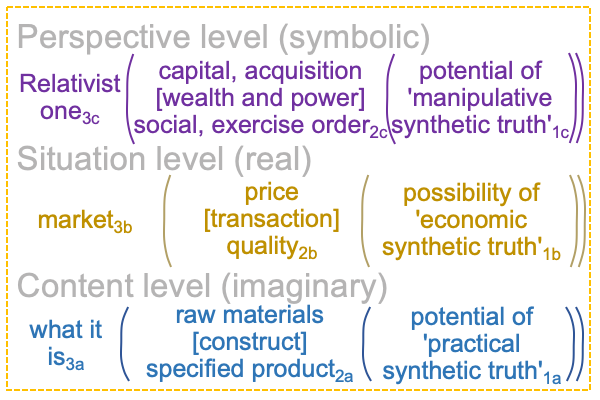
On the symbolic level, the normal context of the Legal One3c brings the actuality of the dyad, {acquire citizenship [wealth and power] exercise order within jurisdiction}2c, into relation with jouissance1c, the potential of ‘a synthetic truth’1c.
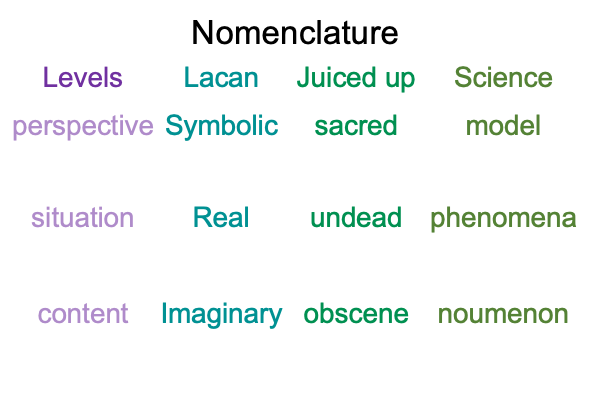
0247 What about Lacan’s terminology?
First, since jouissance1c belongs to the perspective level and since the logic of firstness is inclusive and allows contradictions, then the virtual nested form in the category of firstness is very much alive.
Perspective-level jouissance1c virtually brings the situation-level potential of ‘identifying location’1b (in the normal context of the subject’s birthplace3b) into relation with the content-level potential of ‘copulation and conception’1a.
Indeed, Miguel and Gabriela, as foreigners, are not supposed to do what citizens are supposed to do because… well… the jurisdiction’s synthetic truth1c does not account for certain possibilities1a.
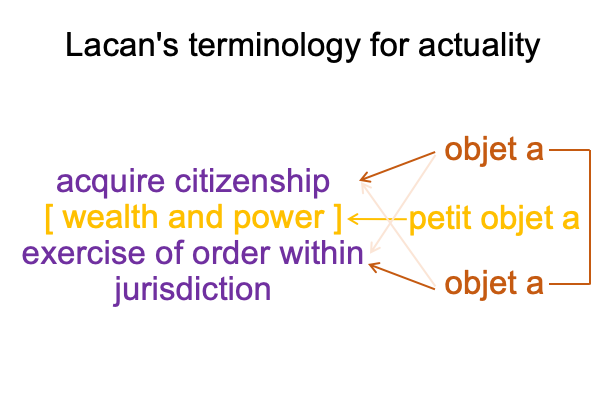
0248 Previously, Lacan’s terminology with respect to secondness applies to the perspective level. Objet a2c emerges from (and situates) jouissance1c and is shown in the following diagram.
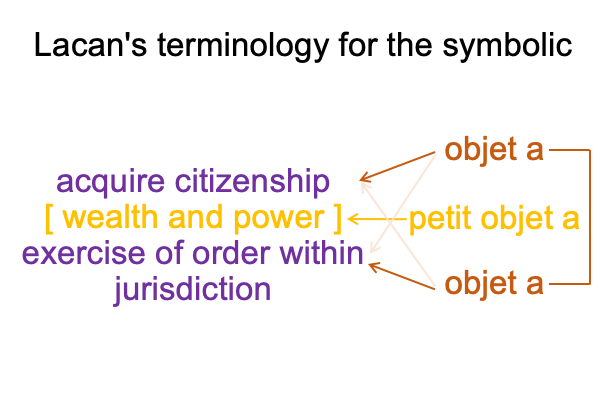
[The citizen’s birthright] expresses [wealth and power]. [It] is the substance between acquisition2c and the exercise of order2c. [It] is a petit objet a, a clue to the realness of the objet a2c.
0249 Lacan’s terminology is reproduced, like a fractal pattern on a higher level of organization, by the three-level interscope, in the following manner.
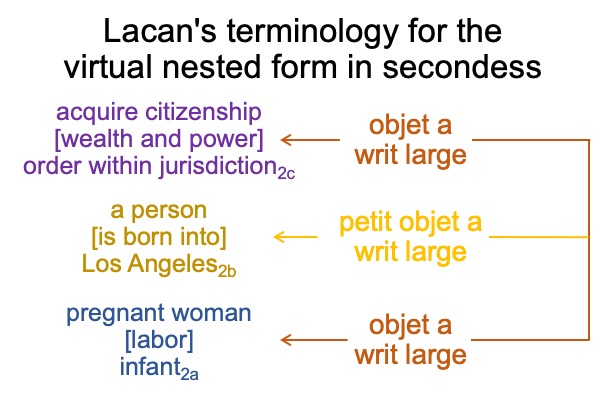
0250 Today, when I walk though a mall near the Pallisades, everyone sees a person [born into] Los Angeles2b. My own presence2b is a clue that I am a legal citizen2c and have a mother who went into labor, years ago2a. Everyone witnesses this particular person shopping, like everyone else, as a petit objet a writ large. They presume that the petit objet a writ large signals an objet a writ large.
No one asks me, “Are you a citizen of Los Angeles?”, unless they have taken an oath of office to do so.
No one asks me, “Have you repaid your mother for her investment in gestation and labor to manufacture you?”. Who would be so rude?
0251 In short, the virtual nested form in the category of secondness appears to be a dyadic actuality writ large. It is like a juiced up version of the perspective-level actuality2c.
To me, this accounts for (in part), why Lacan, and Zizek following the master, introduce juiced up terminology, forcing the inquirer to see the three levels of imaginary, real and symbolic from an alternate point of view. Think parallax! Or maybe, think fractal! How about “think shifty”?
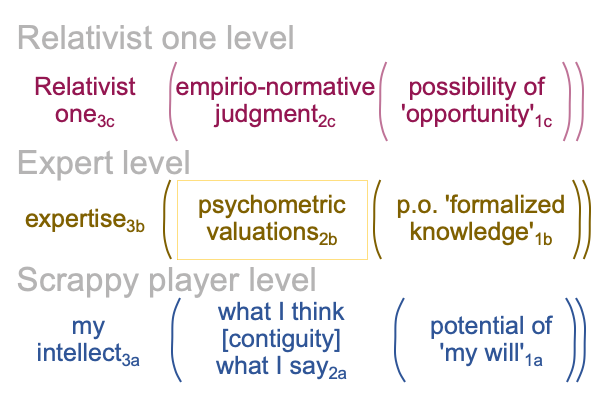
0252 Indeed, to me, it seems that Zizek’s Christian atheism is made possible through a psychoanalytic technique, involving shifting locations within a content-level object2a, corresponding to {what I think [contiguity] what I say}2a.
Or, something like that.
Hmmm.
Is there a container2a within which this opportunistic shifting of points of view takes place?
0253 Is it the analytic dyad?
Or is it… hmmm?