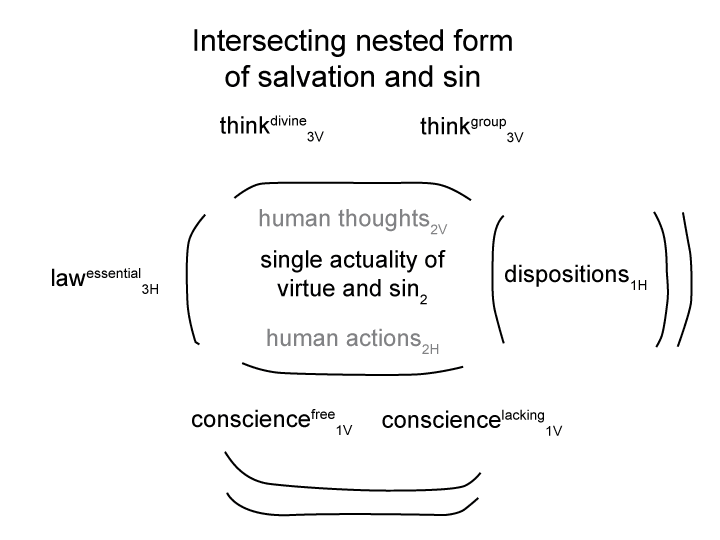
Man and Sin by Piet Schoonenberg (1964) 1.7J
Summary of text [comment] pages 47, 48 and 49
Does sin affect God?
The Scriptures say yes. God emotionally reacts to provocation and disdain. God may be rash, slow to anger, and regret prior stances. Yahweh exhibits anger, pity, jealousy and commitment.
But does that mean that sin affects God?
From the Greek point of view [a linear development of ideas honing the possibility of recognition], God’s majesty and transcendence implies that He endures no injury and no harm.