Looking at Vic Norris and Alexei Sharov’s Chapter (2024) “…How Bacterial Cells… Change… in Response to Various Signals” (Part 4 of 4)
0680 Now I can draw another association between category-based nested forms.
0681 If biosemiotics is what all biological processes have in common, and if the authors are biologists who both study and participate in biological processes, then a technical discussion concerning how bacterial regulate their functions in response to various signals should contain a certain irony.
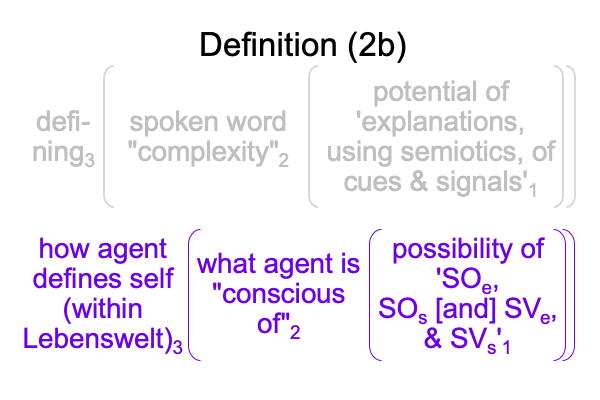
0682 So, it is no surprise that these biosemiotic researchers define3 “complexity”2 as situating the potential of ‘biological explanations of bacterial cues and signals using semiotics’1.
0683 The normal context of definition3 compares to how any biological organism defines itself within its Umwelt3.
0684 The actuality of the spoken word, “complexity”2, compares to what any biological organism is figuratively “conscious of”2 (especially in regards to a model of the Cellular Basis of Consciousness). Or maybe, “complexity” describes what we are conscious of when we regard the semiotic interplay within any biological organism.
Plus, in the discussion section (14.5), “complexity” touches base with the “subjective experience” of an organism, from the point of view of a disinterested observer (the biosemiotician) looking in. Perhaps, the organism is “conscious” of its “phenotype”.
0685 The potential of ‘explanations (meaning) of cues & signals (message) using semiotics (presence)’1 compares to the potential of ‘identity (meaning), competitive coherence (presence) and events within the Umwelt (message)’1 for any biological organism.
0686 Surely, this implies that Norris and Sharov’s hypothesis applies to any biological organism, not just bacteria.
How so?
In points 0634 and 0635, the category-based nested form for definition meshes with the actuality2 of semiotic agency.
Here is the same diagram applied to the bacterium.
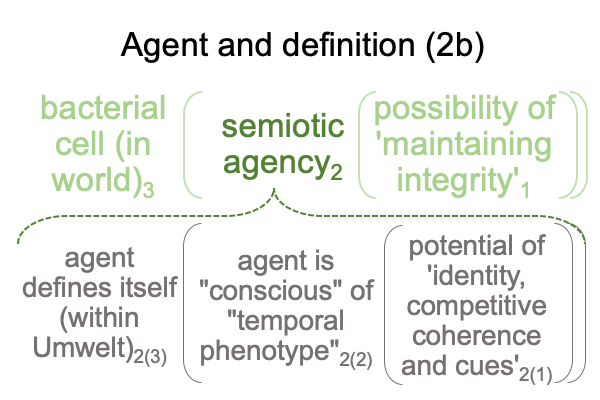
Does it seem that speech-alone talk infiltrates semiotic agency?
It is as if a bacterium3 speaks2 its identity1.
0687 At the same time, I must keep in mind that biosemiotics dwells in the house of science.
Sharov and Tonnessen’s noumenal overlay, that is semiotic agency2, is objectified by biological phenomena in regards to meaning, presence and message1. Or, should I say, “…in regards to SOe, SOs [&] SVe, and SVs.”?
These phenomena (what is for the Positivist’s judgment) are observed and measured in order to produce models using the disciplinary languages (including diagrams) of biosemiotics (what ought to be for the Positivist’s judgment).
All this occurs under the auspices of a positivist intellect (relation for the Positivist’s judgment) who would rather do without metaphysics But hey, semiotic agency2 is an actuality2 within a triadic relation. Without a normal context3and potential1 for semiotic agency2, biosemiotics simply does not register.
0688 Perhaps, “the temporal phenotype that the agent seems to be conscious of”2(2) corresponds to what needs to be explained in the S&T noumenal overlay. If so, then the agent is “conscious” by way of its specifying and exemplar sign-interpretants (SIs and SIe).
That is to say, two sign-interpretants constitute an organism’s figurative “consciousness”.
Surely, these sign-interpretants3((1)) cannot be reduced to actuality2 because they reside outside of Peirce’s category of secondness. However, because the entire nested form in the above figure meshes with the actuality of semiotic actuality2, these sign-interpretants3((1)) are incorporated into the realm of secondness2 by an agent3 (say, a bacterium) on the basis of the potential of ‘a final causality’1.
So, what does a scientist do?
The scientist reaches for the label, “complexity”.
It is sort like asking a familiar civilized term to execute a tricky cognitive manipulation.
0689 Who would anticipate that?
Surely, Vic Norris and Alexei Sharov propose a worthy hypothesis on on how bacterial cells sustain and change their lives in response to various signals. The phenomenon of competitive coherence is worth elevating, along with the phenomena of identity and cues within the Umwelt. These phenomena are observable and measurable sign-elements ofthe S&T noumenal overlay.
0690 At the end, I am left with the ambiguity of “definition”.
What compares to definition?
In general, the normal context of definition3 brings the actuality of a spoken word (or term)2 into relation with the potential of meaning, presence and message1.
For this chapter, the normal context of the agent defining itself with its Umwelt2(3) brings the actuality that the agent is “conscious” of its “phenotype”2(2) into relation with the potentials of ‘identity (meaning), competitive coherence (presence) and signals and cues (message)’2(1).
For the unfolded empirio-schematic judgment, the normal context of disciplinary language3 brings the actuality of (complex) models for “the phenotype”2 into relation with the potential of ‘observations and measurements of biological phenomena’1.
0691 Here is a picture of the last two category-based nested forms in the previous point.
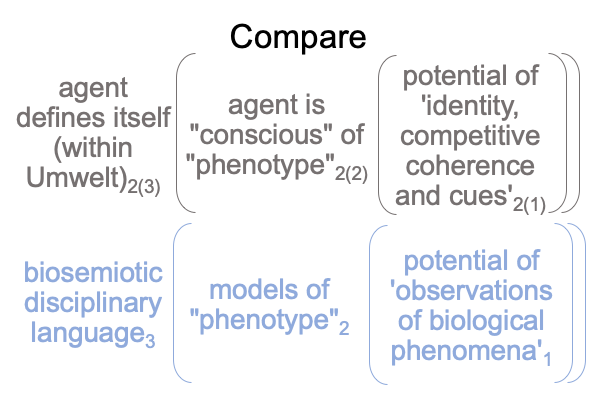
Clearly, a comparison between a definition that meshes with semiotic agency and the empirio-schematic judgment is provocative.
Yet, that provocation is in tune with the author’s proposal.
0692 That proposal is constructed with spoken words.
Speech-alone talk can label anything. And, now we can label the meanings, presences and messages within biological organisms as if they are phenomena. We can also model our observations and measurements of these phenomena using spoken words that describe what needs to be explained, the sign-interpretants themselves.
0693 Here is one implication.
Biosemiotics is the field of inquiry3 that brings definitions that mesh with semiotic agency2 into relation with the potential of empirio-schematic inquiry1.
Perhaps, this is why the field of biosemiotics seems to be older than science as configured by modern Positivists (beginning with the mechanical philosophers of the 1600s).
And younger.
0694 For the modern Positivists, empirio-schematic inquiry (what ought to be, secondness) belongs to the realm of actuality and the noumenon [and] its phenomena (what is, firstness) belongs to the realm of possibility.
For the postmodern biosemiotician, empirio-schematic inquiry opens up to the categories of thirdness and firstness,which are the same categories encountered in Aristotle’s formal and final causalities.
The implications are difficult to fathom.
0695 I thank the authors for this chapter and hope this examination adds value to their inquiries.
