Biosemiotics and the Origins of Life on Earth (Part 1 of 8)
0271 What does biosemiotics have to say about abiogenesis, the origin of life from non-living matter?
0272 Two texts are before me.
0273 Semiotic Agency: Science Beyond Mechanism is written by biosemioticians Alexei Sharov and Morten Tonnessen. Semiotic Agency is published in 2021 by Springer and logs in at volume 25 of Springer’s Series in Biosemiotics. Series editors have Razie Mah’s permission for use of the following disquisition, with attribution of said blogger.
The text is open to chapter five, titled, “Origins of Life”, and is found on pages 123-149. This chapter closes Part II of Semiotic Agency. The title of Part II is “Agency in Organisms and Beyond.”
0274 Pathways to the Origin and Evolution of Meaning in the Universe is edited by Alexei Sharov and George Mikhailovsky (2024, Scrivener Press, Beverly MA).
The text is open to chapter nine, titled “Chemical Origins of Life, Agency and Meaning” (pages 189-210). This chapter opens Part II, titled “Meanings in the Evolution of Life”. The chapter’s author is Alexei Sharov.
0275 First and foremost, chemistry-based scenarios for the origins of life have proven futile. Why? For one, it is difficult to imagine a chemical system constituting a semiotic agent. Sure, a biological agent can be reduced to a chemical soup, but a chemical soup cannot unreduced to a biological being.
Is this the reason why proposals of life emerging from a primordial soup consistently fail?
0276 The key word in the above paragraph is “emerging”.
0277 So why not turn to Mariusz Tabaczek, who writes two books, titled Emergence (2019) and Divine Action and Emergence (2021) that are reviewed in Razie Mah’s blog for April and May, 2024? These and other examinations go into Razie Mah’s two-part e-book, Comments on Mariusz Tabaczek’s Arc of Inquiry (2019-2024), available at smashwords and other e-book venues.
0278 Tabaczek criticizes Terrence Deacon, even as he translates Deacon’s conceptual apparatus into a classical Aristotelian framework. Why? If Deacon borrows ideas from Aristotle and re-tools them for his own approach to emergent systems, then why not articulate Deacon’s approach using Aristotle’s terms?
0279 The answer turns out to be more than academic.
Recall the Positivist’s judgment for the natural sciences?
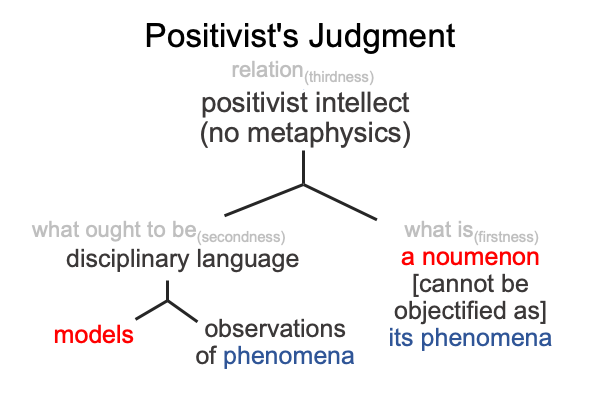
The noumenon (the thing itself) and the model (what ought to be for the empirio-schematic judgment) are two contending sources of illumination. Deacon stands with the model, then uses modified versions of Aristotle’s vocabulary in order to project his model onto the noumenon. In contrast, Tabaczek stands with the noumenon, where Aristotle’s terminology is at home. He sees Deacon’s projection from the model back onto the noumenon and does not think too highly of the imposition.