Looking at Mariusz Tabaczek’s Book (2024) “Theistic Evolution” (Part 1 of 21)
0644 The full title of the book before me is Theistic Evolution: A Contemporary Aristotelian-Thomistic Perspective(Cambridge University Press: Cambridge: UK). The book arrives on my doorstep in October 2023. The copyright is dated 2024.
How time flies.
0645 This examination builds on previous blogs and commentaries.
Here is a picture.

0646 A quick glance backwards is appropriate.
Tabaczek’s story begins in the waning days of the Age of Ideas, when the Positivist’s judgment once thrived.
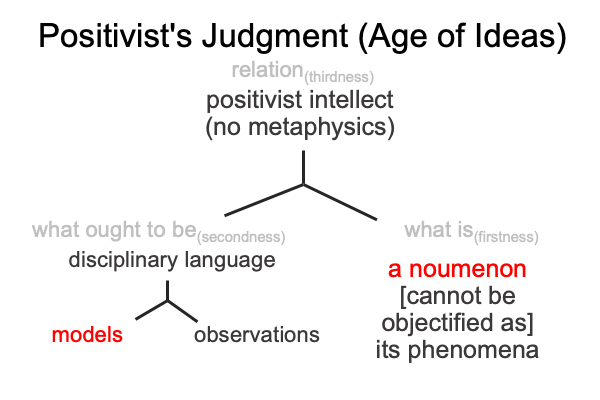
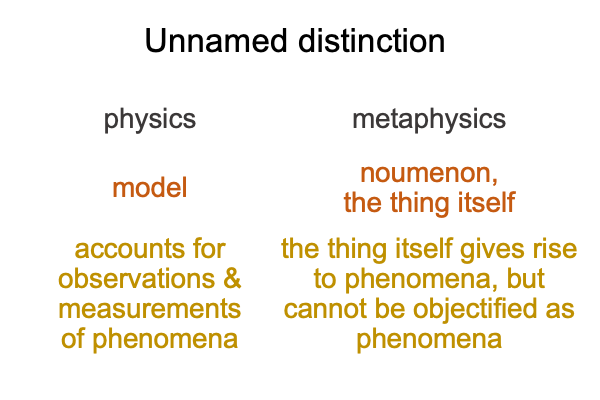
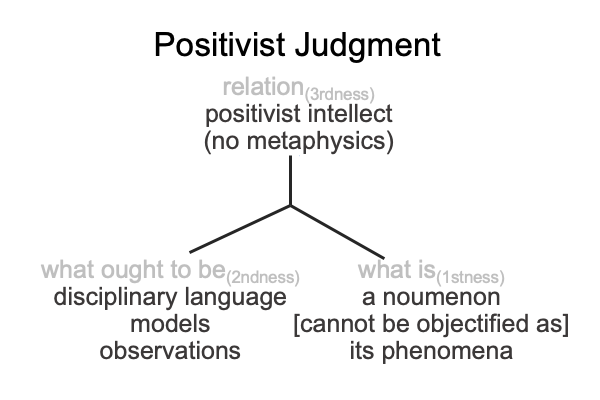
0647 The Positivist judgment holds two sources of illumination. Models are scientific. Noumena are the things themselves. Physics applies to models. Metaphysics applies to noumena. So, I ask, “Which one does the positivist intellect elevate over the other?”
The answer is obvious.
So, the first part of the story is that the positivist intellect dies, and lives on as a ghost (points 0001-0029).
0648 Tabaczek buries the positivist intellect and places the two sources of illumination against one another. It is as if they reflect one another.
But, the two sources also have their advocates.
In Emergence, Tabaczek argues that models of emergence require metaphysical styles of analysis.
In Divine Action and Emergence, he sets out to correct metaphysical emanations reflecting scientific models of emergence. It is as if these emanations are reflections of science in the mirror of theology. Intellectuals inspired by science want to see ‘what is’ of the Positivist’s judgment in the mirror of theology. But, note the difference between the picture of the Positivist’s judgment and the two hylomorphes in Tabaczek’s mirror (points 0039-0061).
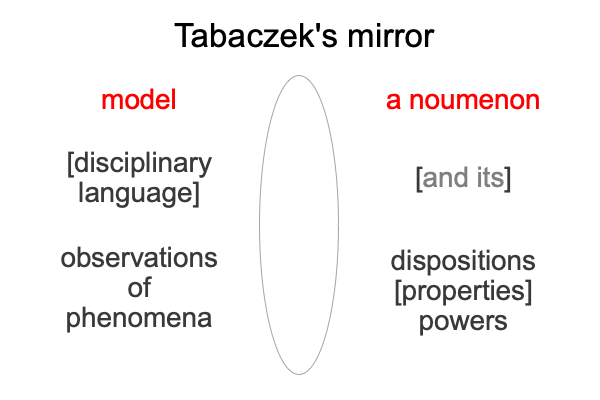
0649 Why do I mention this?
In the introduction of the book before me, Tabaczek discusses his motivations. He, as a agent of theology, wants to exploit an opportunity. That opportunity is already present in the correction that he makes to what an agent of science sees in the mirror of theology (pictured below).
0650 What an opportunity!
Tabaczek offers the hope of a multidimensional, open-minded, and comprehensive (say nothing of comprehensible) account of evolutionary theory.
How so?
The positivist intellect is dead. The positivist intellect ruled the Positivist’s judgment with the maxim, “Metaphysics is not allowed.”
0651 Now that the positivist intellect is dead, the two illuminations within the former Positivist’s judgment may transubstantiate into the realm of actuality and become two hylomorphes, standing like candles that reflect one another in Tabaczek’s mirror.
Tabaczek, as an agent of theology, witnesses how a scientist views himself in the mirror of theology. The scientist sees the model as more real than the noumenon (the thing itself, which cannot be objectified as its phenomena). Indeed, the scientist projects ‘what is’ of the Positivist’s judgment into the mirror of theology.
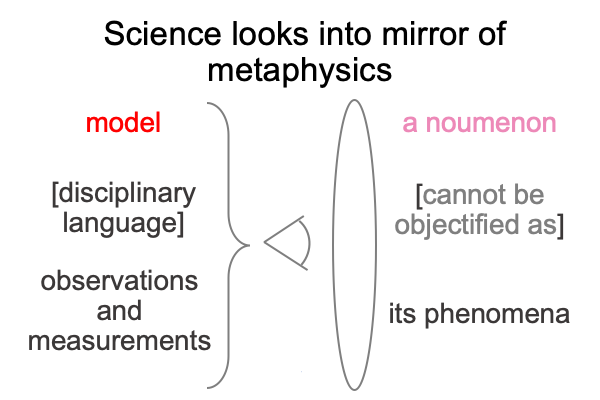
0652 Tabaczek wants to project his philosophical construction of the noumenon (in concert with its dispositions and powers, as well as its matter and form) into the mirror of science.
But, I wonder whether any agent of science is willing to stop listening to the ghost of the positivist intellect long enough to discern what theologians project into the mirror of science.
0653 Yes, Tabaczek’s inquiry is all about optics.
0654 So, who are the players involved in the intellectual drama of Tabaczek’s mirror.
Tabaczek identifies three.
To me, there must be four.
0655 The first is the agent of science. The scienceagent is the one that makes the models. Two types of scienceagent stand out in the study of biological evolution: the natural historian and the geneticist.
0656 The second is the agent of theology. Tabaczek limits theologyagents to experts in Aristotle (384-322 B.C.) and Thomas Aquinas (1225-1274 A.D.).
In a way, this self-imposed limit is a handicap, since Aristotle and Aquinas philosophize long before Darwin publishes On The Origin of Species (1859).
In another way, this self-imposed limit is a blessing, since it provides me with an occasion for examining his argument from the framework of Charles S. Peirce (1839-1914). According to the semiotician and Thomist John Deely (1942-2017), Peirce is the first postmodern philosopher. Peirce is also a co-discoverer of the triadic nature of signs, along with the Baroque scholastic (that is Thomist) John Poinsot (1589-1644), otherwise known as John of Saint Thomas.
Peirce’s semiotics begins where Baroque scholasticism leaves off.
0657 The third is the image that the scientist projects into the mirror of theology. I label this image: theologymirror, in contrast to scienceagent. The theologyagent can see the image in theologymirror, but is not the source of that image. I have already shown the initial image that the agent of science sees in the mirror of theology. I have also noted that Tabaczek aims to correct that projection.
0658 The fourth is the image that the theologian casts into the mirror of science. I label this image: sciencemirror, in contrast to theologyagent. The scienceagent can see the image in sciencemirror, but is not the source of that image. I have already indicated that the scienceagent (more or less) does not care what is in sciencemirror, because the ghost of the positivist intellect whispers in the ear of scienceagent, “All that metaphysical stuff is completely unnecessary.”